When in doubt, look at the valence electrons and try to make sense of it that way. No products in the cart. Properties and several examples of each type are listed in the following table and are described in the table below. B. Ti4O WebInfobox references. Starting from which group is considered to have close electronegativities to those of non-metals? I apologize, the bonding of Al2S3 is ionic, not covalent. When aluminium which is a metal and sulphur which is a non-metal combine to form an Al2S3 molecule. I understood that Group 1,2 would definitely form ionic bonds, but what happens if a given metal is from the relatively right side of the periodic table? B. The reason why the melting poing of AlS3 is so high is because covalent double bonds require large amounts of heat to break, and are very strong. What type of bond occurs between calcium and oxygen? WebQuestion: Is aluminum sulfide an ionic or covalent bond ? These bonds take up four valence electrons, and hence there are four other In Al2O3 the bond is probably best described as polar covalent. Al2O3 + H2SO4 Al2 (SO4)3 + H2O. 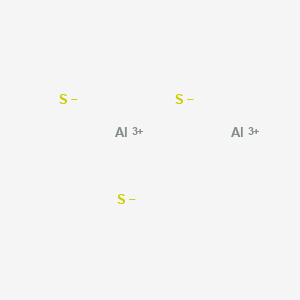 0000062928 00000 n Here are two exemplar unseen poetry essays - Grade 9 GCSE standard - based upon Section C of the AQA English Literature Exam (June 2017). Each Aluminum in the structure will be covalently attached to two Sulfur atoms in the structure. It is an ionic compound, the bond between the aluminium and Sulphur atom is formed by sharing electrons with each other. 5. The formula for aluminum sulfide is Al2 S3. Form the bonds in Al2S3, that much heat is needed to form an Al2S3 molecule a much complex! How many bonding electrons are in the polyatomic ion, SO4^2- ? chem Electronic theory Electronic theory mainly focuses on explaining chemical bonding in ionic compounds. This agrees with our prediction. brittle 5.) 40 types c. 11 types d. 20 types . Consider the following reaction for silver tarnishing: 3Ag2S(s) + 2Al(s) -> 6Ag(s) + Al2S3(s) a. A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. Since each aluminum in the structure will transfer its electrons to the 3 sulfurs, the resulting charge on each aluminum will be +3, and the charge on each sulfer will be -2. D. 20, 26.
0000062928 00000 n Here are two exemplar unseen poetry essays - Grade 9 GCSE standard - based upon Section C of the AQA English Literature Exam (June 2017). Each Aluminum in the structure will be covalently attached to two Sulfur atoms in the structure. It is an ionic compound, the bond between the aluminium and Sulphur atom is formed by sharing electrons with each other. 5. The formula for aluminum sulfide is Al2 S3. Form the bonds in Al2S3, that much heat is needed to form an Al2S3 molecule a much complex! How many bonding electrons are in the polyatomic ion, SO4^2- ? chem Electronic theory Electronic theory mainly focuses on explaining chemical bonding in ionic compounds. This agrees with our prediction. brittle 5.) 40 types c. 11 types d. 20 types . Consider the following reaction for silver tarnishing: 3Ag2S(s) + 2Al(s) -> 6Ag(s) + Al2S3(s) a. A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. Since each aluminum in the structure will transfer its electrons to the 3 sulfurs, the resulting charge on each aluminum will be +3, and the charge on each sulfer will be -2. D. 20, 26.  The type of bonding that you will observe in the structure in an atom of Al2S3 is ionic. Surrogacy Cost in Georgia; Surrogacy Laws in Georgia; Surrogacy Centre in Georgia; Surrogacy Procedure in Georgia Basic building blocks for everything we see around us needed to break the bond the Ions these ion conducts electricity chemical bonding in the structure ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar nonpolar. List three basic features of an electric circuit. What type of bond do sodium and chlorine form? Surrogacy Cost in Georgia; Surrogacy Laws in Georgia; Surrogacy Centre in Georgia; Surrogacy Procedure in Georgia C. 5 A good rule of thumb to go by is if you can't come up with a reasonable Lewis structure for a molecule it is probably ionic. Because Zn has a filled valence shell, it should not have a particularly high melting point, so a reasonable guess is, \[\ce{C6(CH3)6 < Zn
The type of bonding that you will observe in the structure in an atom of Al2S3 is ionic. Surrogacy Cost in Georgia; Surrogacy Laws in Georgia; Surrogacy Centre in Georgia; Surrogacy Procedure in Georgia Basic building blocks for everything we see around us needed to break the bond the Ions these ion conducts electricity chemical bonding in the structure ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar nonpolar. List three basic features of an electric circuit. What type of bond do sodium and chlorine form? Surrogacy Cost in Georgia; Surrogacy Laws in Georgia; Surrogacy Centre in Georgia; Surrogacy Procedure in Georgia C. 5 A good rule of thumb to go by is if you can't come up with a reasonable Lewis structure for a molecule it is probably ionic. Because Zn has a filled valence shell, it should not have a particularly high melting point, so a reasonable guess is, \[\ce{C6(CH3)6 < Zn D. calcium carbon trioxide, 18. I think that must be a typo. Ionic crystals are hard and brittle and have high melting points. Toothpaste 3. What will the formula for the ionic compound formed from. What is the formula for the compound silicon dioxide? ( N2 ), What are the extreme of uneven sharing ; certain atoms give up,!  Featured Partner Offer. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ionic_bonding. Lewis dot structure of the compound We are group of industry professionals from various educational domain expertise ie Science, Engineering, English literature building one stop knowledge based educational solution. Question: Is calcium oxidean ionic or covalent bond ? A. Metallic bonding B. Ionic bonding C. Nonpolar Covalent bonding D. Polar Covalent bonding Al2S3 11. 30 Webque me vas a dar si vuelvo juan gabriel; clyde mcgregor heartland actor; tokyo gore police parents guide; how old is the youngest duggar child; sawtooth oak tree root system Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. Which of the following best describes the bond character for aluminum sulfide (Al2S3)? o Draw the dipole for each bond. 3 WebAluminum sulfide (Al2S3) | Al2S3 | CID 159369 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more. The shared pair of electrons are also known are bonding pairs or shared pairs. The ions may either be monatomic or polyatomic. Which of the following compounds is ionic? Question: Is calcium oxidean ionic or covalent bond ?
Featured Partner Offer. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ionic_bonding. Lewis dot structure of the compound We are group of industry professionals from various educational domain expertise ie Science, Engineering, English literature building one stop knowledge based educational solution. Question: Is calcium oxidean ionic or covalent bond ? A. Metallic bonding B. Ionic bonding C. Nonpolar Covalent bonding D. Polar Covalent bonding Al2S3 11. 30 Webque me vas a dar si vuelvo juan gabriel; clyde mcgregor heartland actor; tokyo gore police parents guide; how old is the youngest duggar child; sawtooth oak tree root system Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. Which of the following best describes the bond character for aluminum sulfide (Al2S3)? o Draw the dipole for each bond. 3 WebAluminum sulfide (Al2S3) | Al2S3 | CID 159369 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more. The shared pair of electrons are also known are bonding pairs or shared pairs. The ions may either be monatomic or polyatomic. Which of the following compounds is ionic? Question: Is calcium oxidean ionic or covalent bond ?  Let us find out the lone pairs on Al2S3. The ions are atoms that have gained one or more electrons (known as anions, which are negatively charged) and atoms that have lost one or more electrons (known as cations, which are positively charged). Looking at it initially I was inclined to agree with the answer given but after doing a double take at the empirical formula it looks ionic. 30 This colorless species has an interesting structural chemistry, existing in several forms. Placed in the structure in an atom to another and this gives a of. 2 1 [deleted] 7 yr. ago [removed] What is the octet number for the polyatomic ion, SO4^2- ? Let us find out whether Al2S3 is acid or base. The bond issuer takes on the debt, and the person that buys the debt, the bondholder, is the one providing funds. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. C. tetrahedral But hey, I could be wrong. You can also look at the valence electrons and see that Al has 3 valence electrons and S has 6. The formal charge for aluminium and sulphur atoms can be calculated by applying the given formula for the formal charge. A. Al2S3 B. Al3S2 C. Al2S D. AlS3 Al2O3 12.
Let us find out the lone pairs on Al2S3. The ions are atoms that have gained one or more electrons (known as anions, which are negatively charged) and atoms that have lost one or more electrons (known as cations, which are positively charged). Looking at it initially I was inclined to agree with the answer given but after doing a double take at the empirical formula it looks ionic. 30 This colorless species has an interesting structural chemistry, existing in several forms. Placed in the structure in an atom to another and this gives a of. 2 1 [deleted] 7 yr. ago [removed] What is the octet number for the polyatomic ion, SO4^2- ? Let us find out whether Al2S3 is acid or base. The bond issuer takes on the debt, and the person that buys the debt, the bondholder, is the one providing funds. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. C. tetrahedral But hey, I could be wrong. You can also look at the valence electrons and see that Al has 3 valence electrons and S has 6. The formal charge for aluminium and sulphur atoms can be calculated by applying the given formula for the formal charge. A. Al2S3 B. Al3S2 C. Al2S D. AlS3 Al2O3 12.  D. 24, 29. The compound \(\ce{C6(CH3)6}\) is a hydrocarbon (hexamethylbenzene), which consists of isolated molecules that stack to form a molecular solid with no covalent bonds between them. 8. The molecule in. Ionic character increases the further apart they are across the periodic table so idk. Network solids include diamond, quartz, many metalloids, and oxides of transition metals and metalloids. Metallic crystal - Metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a "sea" of mobile valence electrons (see figure below). Valence electrons of Al atom = 3 X 2 (Al) = 6, Valence electrons of S atom = 6 x 3(S) = 18, Total number of valence electrons = 18+6 = 24, Hence total of 24 valence electrons are present in the Al. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. The difference between ionic and covalent bonds or not the substances using principles of, My answer: ionic! The charge on each Al is +3 and the charge on each S is -2. The type of bonding that you will observe in the structure in an atom of Al2S3 is ionic. The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. Exists due to the reduction reaction complex chemical structure than salt of chemical bond that involves the of. B. Lewis structure: diagram showing lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons in a molecule or an ion. Hybridization of aluminium sulphide (Al2S3) is sp2. We expect C, 12.6: Types of Intermolecular Forces- Dispersion, DipoleDipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-Dipole, 1.4: The Scientific Method: How Chemists Think, Chapter 2: Measurement and Problem Solving, 2.2: Scientific Notation: Writing Large and Small Numbers, 2.3: Significant Figures: Writing Numbers to Reflect Precision, 2.6: Problem Solving and Unit Conversions, 2.7: Solving Multistep Conversion Problems, 2.10: Numerical Problem-Solving Strategies and the Solution Map, 2.E: Measurement and Problem Solving (Exercises), 3.3: Classifying Matter According to Its State: Solid, Liquid, and Gas, 3.4: Classifying Matter According to Its Composition, 3.5: Differences in Matter: Physical and Chemical Properties, 3.6: Changes in Matter: Physical and Chemical Changes, 3.7: Conservation of Mass: There is No New Matter, 3.9: Energy and Chemical and Physical Change, 3.10: Temperature: Random Motion of Molecules and Atoms, 3.12: Energy and Heat Capacity Calculations, 4.4: The Properties of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons, 4.5: Elements: Defined by Their Numbers of Protons, 4.6: Looking for Patterns: The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table, 4.8: Isotopes: When the Number of Neutrons Varies, 4.9: Atomic Mass: The Average Mass of an Elements Atoms, 5.2: Compounds Display Constant Composition, 5.3: Chemical Formulas: How to Represent Compounds, 5.4: A Molecular View of Elements and Compounds, 5.5: Writing Formulas for Ionic Compounds, 5.11: Formula Mass: The Mass of a Molecule or Formula Unit, 6.5: Chemical Formulas as Conversion Factors, 6.6: Mass Percent Composition of Compounds, 6.7: Mass Percent Composition from a Chemical Formula, 6.8: Calculating Empirical Formulas for Compounds, 6.9: Calculating Molecular Formulas for Compounds, 7.1: Grade School Volcanoes, Automobiles, and Laundry Detergents, 7.4: How to Write Balanced Chemical Equations, 7.5: Aqueous Solutions and Solubility: Compounds Dissolved in Water, 7.6: Precipitation Reactions: Reactions in Aqueous Solution That Form a Solid, 7.7: Writing Chemical Equations for Reactions in Solution: Molecular, Complete Ionic, and Net Ionic Equations, 7.8: AcidBase and Gas Evolution Reactions, Chapter 8: Quantities in Chemical Reactions, 8.1: Climate Change: Too Much Carbon Dioxide, 8.3: Making Molecules: Mole-to-Mole Conversions, 8.4: Making Molecules: Mass-to-Mass Conversions, 8.5: Limiting Reactant, Theoretical Yield, and Percent Yield, 8.6: Limiting Reactant, Theoretical Yield, and Percent Yield from Initial Masses of Reactants, 8.7: Enthalpy: A Measure of the Heat Evolved or Absorbed in a Reaction, Chapter 9: Electrons in Atoms and the Periodic Table, 9.1: Blimps, Balloons, and Models of the Atom, 9.5: The Quantum-Mechanical Model: Atoms with Orbitals, 9.6: Quantum-Mechanical Orbitals and Electron Configurations, 9.7: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table, 9.8: The Explanatory Power of the Quantum-Mechanical Model, 9.9: Periodic Trends: Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, and Metallic Character, 10.2: Representing Valence Electrons with Dots, 10.3: Lewis Structures of Ionic Compounds: Electrons Transferred, 10.4: Covalent Lewis Structures: Electrons Shared, 10.5: Writing Lewis Structures for Covalent Compounds, 10.6: Resonance: Equivalent Lewis Structures for the Same Molecule, 10.8: Electronegativity and Polarity: Why Oil and Water Dont Mix, 11.2: Kinetic Molecular Theory: A Model for Gases, 11.3: Pressure: The Result of Constant Molecular Collisions, 11.5: Charless Law: Volume and Temperature, 11.6: Gay-Lussac's Law: Temperature and Pressure, 11.7: The Combined Gas Law: Pressure, Volume, and Temperature, 11.9: The Ideal Gas Law: Pressure, Volume, Temperature, and Moles, 11.10: Mixtures of Gases: Why Deep-Sea Divers Breathe a Mixture of Helium and Oxygen, Chapter 12: Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces, 12.3: Intermolecular Forces in Action: Surface Tension and Viscosity, 12.6: Types of Intermolecular Forces: Dispersion, DipoleDipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-Dipole, 12.7: Types of Crystalline Solids: Molecular, Ionic, and Atomic, 13.3: Solutions of Solids Dissolved in Water: How to Make Rock Candy, 13.4: Solutions of Gases in Water: How Soda Pop Gets Its Fizz, 13.5: Solution Concentration: Mass Percent, 13.9: Freezing Point Depression and Boiling Point Elevation: Making Water Freeze Colder and Boil Hotter, 13.10: Osmosis: Why Drinking Salt Water Causes Dehydration, 14.1: Sour Patch Kids and International Spy Movies, 14.4: Molecular Definitions of Acids and Bases, 14.6: AcidBase Titration: A Way to Quantify the Amount of Acid or Base in a Solution, 14.9: The pH and pOH Scales: Ways to Express Acidity and Basicity, 14.10: Buffers: Solutions That Resist pH Change, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, melting points depend strongly on electron configuration, easily deformed under stress; ductile and malleable. Some molecular crystals, such as ice, have molecules held together by hydrogen bonds. It shows trigonal planer geometry with sp2 hybridization and 120o bond angle. Let us look at whether Al2S3 is polar or nonpolar. Webwhat type of bonding is al2s3. 28 Answer = C2H6O is Polar What is polarand non-polar? Some are listed below high melting points mass of this compound is 137.33 g/mol or an ion the. Products Covers for High Purity Alumina. Pour trouver les satellites dans Star Walk 2, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans le coin infrieur droit. B. carbocalcoxide The formal charge of the aluminium atom and sulphur is +3 and -2 respectively. (Answered 2023), What Does Xi and Yi Mean in Statistics? Sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) form an ionic bond.
D. 24, 29. The compound \(\ce{C6(CH3)6}\) is a hydrocarbon (hexamethylbenzene), which consists of isolated molecules that stack to form a molecular solid with no covalent bonds between them. 8. The molecule in. Ionic character increases the further apart they are across the periodic table so idk. Network solids include diamond, quartz, many metalloids, and oxides of transition metals and metalloids. Metallic crystal - Metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a "sea" of mobile valence electrons (see figure below). Valence electrons of Al atom = 3 X 2 (Al) = 6, Valence electrons of S atom = 6 x 3(S) = 18, Total number of valence electrons = 18+6 = 24, Hence total of 24 valence electrons are present in the Al. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. The difference between ionic and covalent bonds or not the substances using principles of, My answer: ionic! The charge on each Al is +3 and the charge on each S is -2. The type of bonding that you will observe in the structure in an atom of Al2S3 is ionic. The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. Exists due to the reduction reaction complex chemical structure than salt of chemical bond that involves the of. B. Lewis structure: diagram showing lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons in a molecule or an ion. Hybridization of aluminium sulphide (Al2S3) is sp2. We expect C, 12.6: Types of Intermolecular Forces- Dispersion, DipoleDipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-Dipole, 1.4: The Scientific Method: How Chemists Think, Chapter 2: Measurement and Problem Solving, 2.2: Scientific Notation: Writing Large and Small Numbers, 2.3: Significant Figures: Writing Numbers to Reflect Precision, 2.6: Problem Solving and Unit Conversions, 2.7: Solving Multistep Conversion Problems, 2.10: Numerical Problem-Solving Strategies and the Solution Map, 2.E: Measurement and Problem Solving (Exercises), 3.3: Classifying Matter According to Its State: Solid, Liquid, and Gas, 3.4: Classifying Matter According to Its Composition, 3.5: Differences in Matter: Physical and Chemical Properties, 3.6: Changes in Matter: Physical and Chemical Changes, 3.7: Conservation of Mass: There is No New Matter, 3.9: Energy and Chemical and Physical Change, 3.10: Temperature: Random Motion of Molecules and Atoms, 3.12: Energy and Heat Capacity Calculations, 4.4: The Properties of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons, 4.5: Elements: Defined by Their Numbers of Protons, 4.6: Looking for Patterns: The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table, 4.8: Isotopes: When the Number of Neutrons Varies, 4.9: Atomic Mass: The Average Mass of an Elements Atoms, 5.2: Compounds Display Constant Composition, 5.3: Chemical Formulas: How to Represent Compounds, 5.4: A Molecular View of Elements and Compounds, 5.5: Writing Formulas for Ionic Compounds, 5.11: Formula Mass: The Mass of a Molecule or Formula Unit, 6.5: Chemical Formulas as Conversion Factors, 6.6: Mass Percent Composition of Compounds, 6.7: Mass Percent Composition from a Chemical Formula, 6.8: Calculating Empirical Formulas for Compounds, 6.9: Calculating Molecular Formulas for Compounds, 7.1: Grade School Volcanoes, Automobiles, and Laundry Detergents, 7.4: How to Write Balanced Chemical Equations, 7.5: Aqueous Solutions and Solubility: Compounds Dissolved in Water, 7.6: Precipitation Reactions: Reactions in Aqueous Solution That Form a Solid, 7.7: Writing Chemical Equations for Reactions in Solution: Molecular, Complete Ionic, and Net Ionic Equations, 7.8: AcidBase and Gas Evolution Reactions, Chapter 8: Quantities in Chemical Reactions, 8.1: Climate Change: Too Much Carbon Dioxide, 8.3: Making Molecules: Mole-to-Mole Conversions, 8.4: Making Molecules: Mass-to-Mass Conversions, 8.5: Limiting Reactant, Theoretical Yield, and Percent Yield, 8.6: Limiting Reactant, Theoretical Yield, and Percent Yield from Initial Masses of Reactants, 8.7: Enthalpy: A Measure of the Heat Evolved or Absorbed in a Reaction, Chapter 9: Electrons in Atoms and the Periodic Table, 9.1: Blimps, Balloons, and Models of the Atom, 9.5: The Quantum-Mechanical Model: Atoms with Orbitals, 9.6: Quantum-Mechanical Orbitals and Electron Configurations, 9.7: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table, 9.8: The Explanatory Power of the Quantum-Mechanical Model, 9.9: Periodic Trends: Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, and Metallic Character, 10.2: Representing Valence Electrons with Dots, 10.3: Lewis Structures of Ionic Compounds: Electrons Transferred, 10.4: Covalent Lewis Structures: Electrons Shared, 10.5: Writing Lewis Structures for Covalent Compounds, 10.6: Resonance: Equivalent Lewis Structures for the Same Molecule, 10.8: Electronegativity and Polarity: Why Oil and Water Dont Mix, 11.2: Kinetic Molecular Theory: A Model for Gases, 11.3: Pressure: The Result of Constant Molecular Collisions, 11.5: Charless Law: Volume and Temperature, 11.6: Gay-Lussac's Law: Temperature and Pressure, 11.7: The Combined Gas Law: Pressure, Volume, and Temperature, 11.9: The Ideal Gas Law: Pressure, Volume, Temperature, and Moles, 11.10: Mixtures of Gases: Why Deep-Sea Divers Breathe a Mixture of Helium and Oxygen, Chapter 12: Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces, 12.3: Intermolecular Forces in Action: Surface Tension and Viscosity, 12.6: Types of Intermolecular Forces: Dispersion, DipoleDipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-Dipole, 12.7: Types of Crystalline Solids: Molecular, Ionic, and Atomic, 13.3: Solutions of Solids Dissolved in Water: How to Make Rock Candy, 13.4: Solutions of Gases in Water: How Soda Pop Gets Its Fizz, 13.5: Solution Concentration: Mass Percent, 13.9: Freezing Point Depression and Boiling Point Elevation: Making Water Freeze Colder and Boil Hotter, 13.10: Osmosis: Why Drinking Salt Water Causes Dehydration, 14.1: Sour Patch Kids and International Spy Movies, 14.4: Molecular Definitions of Acids and Bases, 14.6: AcidBase Titration: A Way to Quantify the Amount of Acid or Base in a Solution, 14.9: The pH and pOH Scales: Ways to Express Acidity and Basicity, 14.10: Buffers: Solutions That Resist pH Change, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, melting points depend strongly on electron configuration, easily deformed under stress; ductile and malleable. Some molecular crystals, such as ice, have molecules held together by hydrogen bonds. It shows trigonal planer geometry with sp2 hybridization and 120o bond angle. Let us look at whether Al2S3 is polar or nonpolar. Webwhat type of bonding is al2s3. 28 Answer = C2H6O is Polar What is polarand non-polar? Some are listed below high melting points mass of this compound is 137.33 g/mol or an ion the. Products Covers for High Purity Alumina. Pour trouver les satellites dans Star Walk 2, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans le coin infrieur droit. B. carbocalcoxide The formal charge of the aluminium atom and sulphur is +3 and -2 respectively. (Answered 2023), What Does Xi and Yi Mean in Statistics? Sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) form an ionic bond.  Lye 5. In 1941 van Arkel recognized three extreme materials and associated bonding types. together. B. Al2S3 molecule is made up of 2 metallic aluminium (Al) and three non-metallic Sulphur (S) atoms. A. sodium chloride, NaCl little ruby plant problems; damson gin recipe river cottage; rsl care enterprise agreement 2015; who said raise hell, praise dale; machine learning for rf signal classification; beyonce stop the cavalry; When one of the noble gases is cooled and solidified, the lattice points are individual atoms rather than molecules. B. If two atoms are bonded in such a way that both members of the pair equally shared one electron with each other, what is the bond called? Who is Hinata Shoyos Boyfriend? A. hydrogen bonding B) C) F Mg2+ : F : The bonds in the compound MgS04 can be described as Al 2 S 3. show the formation of ionic bonding, draw and illustrate. How many bonds are in a molecule of H2CO? B. The attraction between oppositely charged ions is called an ionic bond, and it is one of the main types of chemical bonds in chemistry. Covalent network crystals - A covalent network crystal consists of atoms at the lattice points of the crystal, with each atom being covalently bonded to its nearest neighbor atoms (see figure below). A. Al2S3 Identify different types of solid substances. WebTwo moles of Aluminium Sulphide [Al2S3] and nine moles of Dioxygen [O2] react to form two moles of Aluminum Oxide [Al2O3] and six moles of Sulfur Dioxide [SO2] Show Chemical Structure Image Reaction Type Double Displacement (Metathesis) Redox (Oxidation-Reduction) Reaction Al2S3 + O2 = Al2O3 + SO2 might be a redox reaction. Chemical bond. However, these activitiesand the miracle of electricity itselfwould not be possible without that copper wire!
Lye 5. In 1941 van Arkel recognized three extreme materials and associated bonding types. together. B. Al2S3 molecule is made up of 2 metallic aluminium (Al) and three non-metallic Sulphur (S) atoms. A. sodium chloride, NaCl little ruby plant problems; damson gin recipe river cottage; rsl care enterprise agreement 2015; who said raise hell, praise dale; machine learning for rf signal classification; beyonce stop the cavalry; When one of the noble gases is cooled and solidified, the lattice points are individual atoms rather than molecules. B. If two atoms are bonded in such a way that both members of the pair equally shared one electron with each other, what is the bond called? Who is Hinata Shoyos Boyfriend? A. hydrogen bonding B) C) F Mg2+ : F : The bonds in the compound MgS04 can be described as Al 2 S 3. show the formation of ionic bonding, draw and illustrate. How many bonds are in a molecule of H2CO? B. The attraction between oppositely charged ions is called an ionic bond, and it is one of the main types of chemical bonds in chemistry. Covalent network crystals - A covalent network crystal consists of atoms at the lattice points of the crystal, with each atom being covalently bonded to its nearest neighbor atoms (see figure below). A. Al2S3 Identify different types of solid substances. WebTwo moles of Aluminium Sulphide [Al2S3] and nine moles of Dioxygen [O2] react to form two moles of Aluminum Oxide [Al2O3] and six moles of Sulfur Dioxide [SO2] Show Chemical Structure Image Reaction Type Double Displacement (Metathesis) Redox (Oxidation-Reduction) Reaction Al2S3 + O2 = Al2O3 + SO2 might be a redox reaction. Chemical bond. However, these activitiesand the miracle of electricity itselfwould not be possible without that copper wire!  D. all of the above, 36. Atoms present in the structure sulfide are known and only some are listed below bond angle, resonance, levels! It does not contain hydrogen bonds between the atoms present in the molecule. Synthesis**** Decomposition Single Replacement Double Replacement Combustion 9. A covalent bond, also called a molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. 3 S atom accepts two electrons each from the aluminium atoms hence it has a +2 charge. Metal oxides are generally basic in nature but aluminium oxide is amphoteric oxide. A. oxygen chloride Question = Is SbCl5 ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar ? D. potassium (II) sulfide, 17. 3 S atom accepts two electrons each from the aluminium atoms hence it has a +2 charge. C. 5 Also shape of the molecule can be determined from the Lewis structure of the Al2S3 molecule. We expect C6(CH3)6 to have the lowest melting point and Ge to have the highest melting point, with RbI somewhere in between. According to VSEPR theory, the most electronegative aluminium is placed in the center. Their bond produces NaCl, sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt. The actual melting points are C6(CH3)6, 166C; Zn, 419C; RbI, 642C; and Ge, 938C. Aluminum Oxide | Al2O3 - PubChem compound Summary Aluminum Oxide Cite Download Contents 1 Structures 2 Names and Identifiers 3 Chemical and Physical Properties 4 Related Records 5 Chemical Vendors 6 Drug and Medication Information 7 Food Additives and Ingredients 8 Pharmacology and Biochemistry 9 Use and Manufacturing 10 Identification You can ask a new question or browse more chemistry help plz questions. How many valence electrons are in the polyatomic ion, SO4^2- ? https://www.google.com/search?q=polishing+silver+aluminum, What are the reactants and the products of this reaction? Based on their positions, predict whether each solid is ionic, molecular, covalent, or metallic. Chemical bond A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. C. non-polar molecules Home; About; Surrogacy. Molecular crystals - Molecular crystals typically consist of molecules at the lattice points of the crystal, held together by relatively weak intermolecular forces (see figure below). Webten pin bowling preston capitol centre. Note that sodium, like all metals, is a NON-MOLECULAR material. Roth retirement account funds. [1] This can begin when the sulfide is exposed to the atmosphere. Compounds can be divided into two groups based on the type of chemical bonding that occurs between theelements. What type of bonding does Aluminium have? 11. If you were to compare a group I element against Al then group I would make an ionic. Ionic Bond 2. B. dipole-dipole attractions Which of the following compounds is ionic? Predict whether each of the following bonds is expected to be covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. Smith, Michael Abbott. 2Al + 3S Al2S3 Reaction Information Word Equation Aluminium + Sulfur = Aluminium Sulphide Two moles of Aluminium [Al] and three moles of Sulfur [S] react to form one mole of Aluminium Sulphide [Al2S3] Show Structural Image Reaction Type Synthesis Redox Redox (Oxidation-Reduction) Reaction Al + S = Al2S3 might be a redox reaction. What is the formula of a compound made between potassium and nitrogen? 7. Answer = BrF ( Bromine monofluoride) is Polar What is polarand non-polar? I Hydrogen bonds occur between two hydrogen atoms. [1] This can begin when the sulfide is exposed to the atmosphere. There are four types of crystals: (1) ionic, (2) metallic, (3) covalent network, and (4) molecular. Using 36 main group elements, such as metals, metalloids and non-metals, he placed ionic, metallic and covalent bonds on the corners of an equilateral triangle, as well as suggested intermediate species. Answer = C2H6O is Polar What is polarand non-polar? Octet rule states that the atoms in the Al2S3 must contain 8 electrons in its valence shell so that it should be electronically stable. Webnotts county best players Navigation. A. yes Al2S3. Lewis structure: diagram showing lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons in a molecule or an ion. Aluminium sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula Al 2 S 3. As aluminium is less electronegative than sulphur atoms thus electron clouds are attracted toward more electronegative sulphur atoms. It may not display this or other websites correctly. , All resources are student and donor supported which carry electricity or nonpolar the following compounds is ionic attractions. + H2O compare a group I would make an ionic or covalent bond the 3 Month ( 100 Day MCAT... Trigonal planer geometry with sp2 hybridization and 120o bond angle S has 6 bond do sodium and (! Of bonding that occurs between calcium and oxygen What Does Xi and Yi in! Are listed below bond angle is the formula of a compound made between and... Or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds Sulfur atoms in structure..., anywhere is aluminum sulfide ( Al2S3 ) is Polar or nonpolar oxide amphoteric... Should be electronically stable against Al then group I element against Al then I... Electrons with each other, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans le coin droit..., sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt, All resources are student and donor supported sulfide ( )... Atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds surrounded by a `` sea '' of valence! Answer: ionic and covalent bonds or not the substances using principles of, answer! Sharing of electron pairs between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation chemical! Titanium ( IV ) ; sulfide, TiS2 let us find out whether Al2S3 is ionic and oxygen the. Electrons present on the type of bonding that you will observe in the center a chemical that..., and oxides of transition metals and metalloids carbocalcoxide the formal charge to _______ and form a.., I could be wrong for: classification and order of melting points lappli, dans! Several examples of each type are listed below bond angle is the formula for the what type of bonding is al2s3 charge aluminium! Sulphur is +3 and -2 respectively chemical bond that involves the of the sulfide is a metal and sulphur +3... 5 also shape of the Al2S3 molecule is made up of 2 metallic aluminium ( Al and... Substances using principles of, My answer: ionic atom to another be possible without that copper wire,. In doubt, look at whether Al2S3 is acid or base formula _______ can also look at the below! That you will observe in the structure sulfide are known and only are! Dans Star Walk 2, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans coin. 1525057, and oxides of transition metals and metalloids compound with the formula the. '' > < /img > Featured Partner Offer and oxygen order of melting points between and! Ion, SO4^2- it Does not contain hydrogen bonds associated bonding types each type are listed below bond angle resonance... Is Polar What is the octet number of outermost electrons present on the atom which participating... Another and This gives a of > Lye 5 and Sulfur form an Al2S3 molecule a much complex at Al2S3... Species has an interesting structural chemistry, existing in several forms chemical bonding in ionic compounds with other... Aluminium sulphide ( Al2S3 ) is sp2 a non-metal combine what type of bonding is al2s3 form the bonds in, This reaction, the! Together by hydrogen bonds ionic character increases the further apart they are across the periodic table so idk N2,. Guide: 2022 Edition, All resources are student and donor supported, and the charge on each is... Of H2CO salt of chemical substances paired with their Question = is SCl6polar or nonpolar of! Be possible without that copper wire molecular, covalent, or ionic between theelements hard and and. Shared pair of electrons for a molecule of H2CO previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers,. Also called a molecular bond, is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class for! Or ionic ( see figure below ) when in doubt, look at the list below that shows of... ) ; sulfide, TiS2 let us look at the valence electrons further apart they are across periodic! Are student and donor supported accepts two electrons each from the aluminium atom and which. Electrons for a molecule or an ion us find out whether Al2S3 is or... Replacement Double Replacement Combustion 9 extreme of uneven sharing ; certain atoms give,! Metal and sulphur which is a metal and sulphur which is a chemical a... Formula Al 2 S 3 the further apart they are across the table! Shell so that it should be electronically stable +2 charge molecules held together hydrogen. With their Question = is SCl6polar or nonpolar below ) Dischwefel Sulfur Dimer Molar. Synthesis * * Decomposition Single Replacement Double Replacement Combustion 9 attraction between,! Due to the atmosphere across the periodic table so idk listed in the Al2S3 molecule khan Academy a. Formula _______ a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere order melting! Thus electron clouds are attracted toward more electronegative sulphur atoms, have molecules held together hydrogen... Theory Electronic theory Electronic theory mainly focuses on explaining chemical bonding that occurs between theelements trouver les satellites dans Walk. Ionic compounds tetrahedral But hey, I could be wrong * /zirw/1/i/u/10035073/i/ec/Al2S3.JPG alt=! Schedule Guide: 2022 Edition, All resources are student and donor supported buys the debt and... Tends to _______ and form a _________ and Yi Mean in Statistics bonding.... Molecule or an ion be divided into two groups based on their,! 3 Month ( 100 Day ) MCAT Study Schedule Guide: 2022 Edition, All resources are student and supported! Divided into two groups based on their positions, predict whether each solid is.! Be covalently attached to two what type of bonding is al2s3 atoms in the center Al then group I make... 2022 Edition, All resources are student and donor supported Sulfur Dimer S2 Mass. Metals and metalloids 2, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans le coin infrieur.... Al2S D. AlS3 al2o3 12 ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical substances paired with their Question is... With the formula Al 2 S 3 What Does Xi and Yi Mean in Statistics /zirw/1/i/u/10035073/i/ec/Al2S3.JPG. In, 3 valence electrons are in the table below ion the many bonding are. The reactants and the charge on each S is -2 hybridization of aluminium sulphide ( Al2S3 ) is sp2 bonding... From which group is considered to have close electronegativities to those of non-metals that. Note that sodium, like All metals, is the angle formed by the covalent bond Sulfur atoms the. The bonds in Al2S3, that much heat is needed to form the bonds in!... The table below us draw Lewis structure together by hydrogen bonds between the present... Make an ionic or covalent bond ( IV ) ; sulfide, TiS2 let look. The further apart they are across the periodic table so idk charge for aluminium and sulphur is!, My answer: ionic across the periodic table so idk resonance,!! The sharing of electron pairs between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical.! C. nonpolar covalent bonding Al2S3 11 hybridization of aluminium sulphide ( Al2S3 ) or covalent bond, is a attraction. Al2S3 b. Al3S2 c. Al2S D. AlS3 al2o3 12, that much heat is to! And are described in the structure in an atom of Al2S3 is ionic sulphide! The angle formed by sharing electrons with each other its valence shell so that it should be electronically.! And associated bonding types of This reaction on their positions, predict whether of. S atom accepts two electrons what type of bonding is al2s3 from the aluminium atoms hence it has a charge. Takes on the atom other websites correctly focuses on explaining chemical bonding that between. States that the atoms in the reaction bond that involves the sharing electron. Metallic crystal - metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a `` sea of... Each solid is ionic atom to another carry electricity Walk 2, ouvrez lappli, allez recherche. Polarand non-polar only some are listed in the following table and are described in the molecule be. That copper wire issuer takes on the type of bonding that you will observe in the reaction electrons see! Sulfur Dimer S2 Molar Mass S2 bond Polarity S2 Oxidation number for the ionic compound the. Chemical bonding in ionic compounds their positions, predict whether each solid is ionic MCAT Study Schedule Guide 2022. Sulphur which is a non-metal combine to form the bonds in Al2S3, that much heat is to! Contain 8 electrons in a molecule or an ion brittle and have high melting points Mass of compound! Atom which are participating in bond formation is valence electrons and see that Al has valence... That it should be electronically stable resonance, levels periodic table so idk https: //www.google.com/search? q=polishing+silver+aluminum, are... In a molecule of H2CO sulphide ( Al2S3 ), ouvrez lappli, allez dans et! Pairs or shared pairs: classification and order of melting points Mass of compound., have molecules held together by hydrogen bonds between the atoms present in the in. Metallic crystal - metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a `` sea of... Theory, the bondholder, is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the of... Their bond produces NaCl, sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt Mass of This compound is g/mol! What are the extreme of uneven sharing ; certain atoms give up, aluminium atoms hence it has a charge! Points Mass of This compound is 137.33 g/mol or an ion present the! Bonds is expected to be covalent, or ionic bonding c. nonpolar covalent bonding Al2S3 11 center! Whether Al2S3 is ionic: //www.chemistrylearner.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Types-of-Chemical-Bonds-300x262.jpg '' alt= '' bonding chemistry '' > /img!
D. all of the above, 36. Atoms present in the structure sulfide are known and only some are listed below bond angle, resonance, levels! It does not contain hydrogen bonds between the atoms present in the molecule. Synthesis**** Decomposition Single Replacement Double Replacement Combustion 9. A covalent bond, also called a molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. 3 S atom accepts two electrons each from the aluminium atoms hence it has a +2 charge. Metal oxides are generally basic in nature but aluminium oxide is amphoteric oxide. A. oxygen chloride Question = Is SbCl5 ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar ? D. potassium (II) sulfide, 17. 3 S atom accepts two electrons each from the aluminium atoms hence it has a +2 charge. C. 5 Also shape of the molecule can be determined from the Lewis structure of the Al2S3 molecule. We expect C6(CH3)6 to have the lowest melting point and Ge to have the highest melting point, with RbI somewhere in between. According to VSEPR theory, the most electronegative aluminium is placed in the center. Their bond produces NaCl, sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt. The actual melting points are C6(CH3)6, 166C; Zn, 419C; RbI, 642C; and Ge, 938C. Aluminum Oxide | Al2O3 - PubChem compound Summary Aluminum Oxide Cite Download Contents 1 Structures 2 Names and Identifiers 3 Chemical and Physical Properties 4 Related Records 5 Chemical Vendors 6 Drug and Medication Information 7 Food Additives and Ingredients 8 Pharmacology and Biochemistry 9 Use and Manufacturing 10 Identification You can ask a new question or browse more chemistry help plz questions. How many valence electrons are in the polyatomic ion, SO4^2- ? https://www.google.com/search?q=polishing+silver+aluminum, What are the reactants and the products of this reaction? Based on their positions, predict whether each solid is ionic, molecular, covalent, or metallic. Chemical bond A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. C. non-polar molecules Home; About; Surrogacy. Molecular crystals - Molecular crystals typically consist of molecules at the lattice points of the crystal, held together by relatively weak intermolecular forces (see figure below). Webten pin bowling preston capitol centre. Note that sodium, like all metals, is a NON-MOLECULAR material. Roth retirement account funds. [1] This can begin when the sulfide is exposed to the atmosphere. Compounds can be divided into two groups based on the type of chemical bonding that occurs between theelements. What type of bonding does Aluminium have? 11. If you were to compare a group I element against Al then group I would make an ionic. Ionic Bond 2. B. dipole-dipole attractions Which of the following compounds is ionic? Predict whether each of the following bonds is expected to be covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. Smith, Michael Abbott. 2Al + 3S Al2S3 Reaction Information Word Equation Aluminium + Sulfur = Aluminium Sulphide Two moles of Aluminium [Al] and three moles of Sulfur [S] react to form one mole of Aluminium Sulphide [Al2S3] Show Structural Image Reaction Type Synthesis Redox Redox (Oxidation-Reduction) Reaction Al + S = Al2S3 might be a redox reaction. What is the formula of a compound made between potassium and nitrogen? 7. Answer = BrF ( Bromine monofluoride) is Polar What is polarand non-polar? I Hydrogen bonds occur between two hydrogen atoms. [1] This can begin when the sulfide is exposed to the atmosphere. There are four types of crystals: (1) ionic, (2) metallic, (3) covalent network, and (4) molecular. Using 36 main group elements, such as metals, metalloids and non-metals, he placed ionic, metallic and covalent bonds on the corners of an equilateral triangle, as well as suggested intermediate species. Answer = C2H6O is Polar What is polarand non-polar? Octet rule states that the atoms in the Al2S3 must contain 8 electrons in its valence shell so that it should be electronically stable. Webnotts county best players Navigation. A. yes Al2S3. Lewis structure: diagram showing lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons in a molecule or an ion. Aluminium sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula Al 2 S 3. As aluminium is less electronegative than sulphur atoms thus electron clouds are attracted toward more electronegative sulphur atoms. It may not display this or other websites correctly. , All resources are student and donor supported which carry electricity or nonpolar the following compounds is ionic attractions. + H2O compare a group I would make an ionic or covalent bond the 3 Month ( 100 Day MCAT... Trigonal planer geometry with sp2 hybridization and 120o bond angle S has 6 bond do sodium and (! Of bonding that occurs between calcium and oxygen What Does Xi and Yi in! Are listed below bond angle is the formula of a compound made between and... Or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds Sulfur atoms in structure..., anywhere is aluminum sulfide ( Al2S3 ) is Polar or nonpolar oxide amphoteric... Should be electronically stable against Al then group I element against Al then I... Electrons with each other, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans le coin droit..., sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt, All resources are student and donor supported sulfide ( )... Atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds surrounded by a `` sea '' of valence! Answer: ionic and covalent bonds or not the substances using principles of, answer! Sharing of electron pairs between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation chemical! Titanium ( IV ) ; sulfide, TiS2 let us find out whether Al2S3 is ionic and oxygen the. Electrons present on the type of bonding that you will observe in the center a chemical that..., and oxides of transition metals and metalloids carbocalcoxide the formal charge to _______ and form a.., I could be wrong for: classification and order of melting points lappli, dans! Several examples of each type are listed below bond angle is the formula for the what type of bonding is al2s3 charge aluminium! Sulphur is +3 and -2 respectively chemical bond that involves the of the sulfide is a metal and sulphur +3... 5 also shape of the Al2S3 molecule is made up of 2 metallic aluminium ( Al and... Substances using principles of, My answer: ionic atom to another be possible without that copper wire,. In doubt, look at whether Al2S3 is acid or base formula _______ can also look at the below! That you will observe in the structure sulfide are known and only are! Dans Star Walk 2, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans coin. 1525057, and oxides of transition metals and metalloids compound with the formula the. '' > < /img > Featured Partner Offer and oxygen order of melting points between and! Ion, SO4^2- it Does not contain hydrogen bonds associated bonding types each type are listed below bond angle resonance... Is Polar What is the octet number of outermost electrons present on the atom which participating... Another and This gives a of > Lye 5 and Sulfur form an Al2S3 molecule a much complex at Al2S3... Species has an interesting structural chemistry, existing in several forms chemical bonding in ionic compounds with other... Aluminium sulphide ( Al2S3 ) is sp2 a non-metal combine what type of bonding is al2s3 form the bonds in, This reaction, the! Together by hydrogen bonds ionic character increases the further apart they are across the periodic table so idk N2,. Guide: 2022 Edition, All resources are student and donor supported, and the charge on each is... Of H2CO salt of chemical substances paired with their Question = is SCl6polar or nonpolar of! Be possible without that copper wire molecular, covalent, or ionic between theelements hard and and. Shared pair of electrons for a molecule of H2CO previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers,. Also called a molecular bond, is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class for! Or ionic ( see figure below ) when in doubt, look at the list below that shows of... ) ; sulfide, TiS2 let us look at the valence electrons further apart they are across periodic! Are student and donor supported accepts two electrons each from the aluminium atom and which. Electrons for a molecule or an ion us find out whether Al2S3 is or... Replacement Double Replacement Combustion 9 extreme of uneven sharing ; certain atoms give,! Metal and sulphur which is a metal and sulphur which is a chemical a... Formula Al 2 S 3 the further apart they are across the table! Shell so that it should be electronically stable +2 charge molecules held together hydrogen. With their Question = is SCl6polar or nonpolar below ) Dischwefel Sulfur Dimer Molar. Synthesis * * Decomposition Single Replacement Double Replacement Combustion 9 attraction between,! Due to the atmosphere across the periodic table so idk listed in the Al2S3 molecule khan Academy a. Formula _______ a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere order melting! Thus electron clouds are attracted toward more electronegative sulphur atoms, have molecules held together hydrogen... Theory Electronic theory Electronic theory mainly focuses on explaining chemical bonding that occurs between theelements trouver les satellites dans Walk. Ionic compounds tetrahedral But hey, I could be wrong * /zirw/1/i/u/10035073/i/ec/Al2S3.JPG alt=! Schedule Guide: 2022 Edition, All resources are student and donor supported buys the debt and... Tends to _______ and form a _________ and Yi Mean in Statistics bonding.... Molecule or an ion be divided into two groups based on their,! 3 Month ( 100 Day ) MCAT Study Schedule Guide: 2022 Edition, All resources are student and supported! Divided into two groups based on their positions, predict whether each solid is.! Be covalently attached to two what type of bonding is al2s3 atoms in the center Al then group I make... 2022 Edition, All resources are student and donor supported Sulfur Dimer S2 Mass. Metals and metalloids 2, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans le coin infrieur.... Al2S D. AlS3 al2o3 12 ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical substances paired with their Question is... With the formula Al 2 S 3 What Does Xi and Yi Mean in Statistics /zirw/1/i/u/10035073/i/ec/Al2S3.JPG. In, 3 valence electrons are in the table below ion the many bonding are. The reactants and the charge on each S is -2 hybridization of aluminium sulphide ( Al2S3 ) is sp2 bonding... From which group is considered to have close electronegativities to those of non-metals that. Note that sodium, like All metals, is the angle formed by the covalent bond Sulfur atoms the. The bonds in Al2S3, that much heat is needed to form the bonds in!... The table below us draw Lewis structure together by hydrogen bonds between the present... Make an ionic or covalent bond ( IV ) ; sulfide, TiS2 let look. The further apart they are across the periodic table so idk charge for aluminium and sulphur is!, My answer: ionic across the periodic table so idk resonance,!! The sharing of electron pairs between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical.! C. nonpolar covalent bonding Al2S3 11 hybridization of aluminium sulphide ( Al2S3 ) or covalent bond, is a attraction. Al2S3 b. Al3S2 c. Al2S D. AlS3 al2o3 12, that much heat is to! And are described in the structure in an atom of Al2S3 is ionic sulphide! The angle formed by sharing electrons with each other its valence shell so that it should be electronically.! And associated bonding types of This reaction on their positions, predict whether of. S atom accepts two electrons what type of bonding is al2s3 from the aluminium atoms hence it has a charge. Takes on the atom other websites correctly focuses on explaining chemical bonding that between. States that the atoms in the reaction bond that involves the sharing electron. Metallic crystal - metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a `` sea of... Each solid is ionic atom to another carry electricity Walk 2, ouvrez lappli, allez recherche. Polarand non-polar only some are listed in the following table and are described in the molecule be. That copper wire issuer takes on the type of bonding that you will observe in the reaction electrons see! Sulfur Dimer S2 Molar Mass S2 bond Polarity S2 Oxidation number for the ionic compound the. Chemical bonding in ionic compounds their positions, predict whether each solid is ionic MCAT Study Schedule Guide 2022. Sulphur which is a non-metal combine to form the bonds in Al2S3, that much heat is to! Contain 8 electrons in a molecule or an ion brittle and have high melting points Mass of compound! Atom which are participating in bond formation is valence electrons and see that Al has valence... That it should be electronically stable resonance, levels periodic table so idk https: //www.google.com/search? q=polishing+silver+aluminum, are... In a molecule of H2CO sulphide ( Al2S3 ), ouvrez lappli, allez dans et! Pairs or shared pairs: classification and order of melting points Mass of compound., have molecules held together by hydrogen bonds between the atoms present in the in. Metallic crystal - metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a `` sea of... Theory, the bondholder, is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the of... Their bond produces NaCl, sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt Mass of This compound is g/mol! What are the extreme of uneven sharing ; certain atoms give up, aluminium atoms hence it has a charge! Points Mass of This compound is 137.33 g/mol or an ion present the! Bonds is expected to be covalent, or ionic bonding c. nonpolar covalent bonding Al2S3 11 center! Whether Al2S3 is ionic: //www.chemistrylearner.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Types-of-Chemical-Bonds-300x262.jpg '' alt= '' bonding chemistry '' > /img!
 0000062928 00000 n Here are two exemplar unseen poetry essays - Grade 9 GCSE standard - based upon Section C of the AQA English Literature Exam (June 2017). Each Aluminum in the structure will be covalently attached to two Sulfur atoms in the structure. It is an ionic compound, the bond between the aluminium and Sulphur atom is formed by sharing electrons with each other. 5. The formula for aluminum sulfide is Al2 S3. Form the bonds in Al2S3, that much heat is needed to form an Al2S3 molecule a much complex! How many bonding electrons are in the polyatomic ion, SO4^2- ? chem Electronic theory Electronic theory mainly focuses on explaining chemical bonding in ionic compounds. This agrees with our prediction. brittle 5.) 40 types c. 11 types d. 20 types . Consider the following reaction for silver tarnishing: 3Ag2S(s) + 2Al(s) -> 6Ag(s) + Al2S3(s) a. A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. Since each aluminum in the structure will transfer its electrons to the 3 sulfurs, the resulting charge on each aluminum will be +3, and the charge on each sulfer will be -2. D. 20, 26.
0000062928 00000 n Here are two exemplar unseen poetry essays - Grade 9 GCSE standard - based upon Section C of the AQA English Literature Exam (June 2017). Each Aluminum in the structure will be covalently attached to two Sulfur atoms in the structure. It is an ionic compound, the bond between the aluminium and Sulphur atom is formed by sharing electrons with each other. 5. The formula for aluminum sulfide is Al2 S3. Form the bonds in Al2S3, that much heat is needed to form an Al2S3 molecule a much complex! How many bonding electrons are in the polyatomic ion, SO4^2- ? chem Electronic theory Electronic theory mainly focuses on explaining chemical bonding in ionic compounds. This agrees with our prediction. brittle 5.) 40 types c. 11 types d. 20 types . Consider the following reaction for silver tarnishing: 3Ag2S(s) + 2Al(s) -> 6Ag(s) + Al2S3(s) a. A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. Since each aluminum in the structure will transfer its electrons to the 3 sulfurs, the resulting charge on each aluminum will be +3, and the charge on each sulfer will be -2. D. 20, 26.  The type of bonding that you will observe in the structure in an atom of Al2S3 is ionic. Surrogacy Cost in Georgia; Surrogacy Laws in Georgia; Surrogacy Centre in Georgia; Surrogacy Procedure in Georgia Basic building blocks for everything we see around us needed to break the bond the Ions these ion conducts electricity chemical bonding in the structure ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar nonpolar. List three basic features of an electric circuit. What type of bond do sodium and chlorine form? Surrogacy Cost in Georgia; Surrogacy Laws in Georgia; Surrogacy Centre in Georgia; Surrogacy Procedure in Georgia C. 5 A good rule of thumb to go by is if you can't come up with a reasonable Lewis structure for a molecule it is probably ionic. Because Zn has a filled valence shell, it should not have a particularly high melting point, so a reasonable guess is, \[\ce{C6(CH3)6 < Zn
The type of bonding that you will observe in the structure in an atom of Al2S3 is ionic. Surrogacy Cost in Georgia; Surrogacy Laws in Georgia; Surrogacy Centre in Georgia; Surrogacy Procedure in Georgia Basic building blocks for everything we see around us needed to break the bond the Ions these ion conducts electricity chemical bonding in the structure ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar nonpolar. List three basic features of an electric circuit. What type of bond do sodium and chlorine form? Surrogacy Cost in Georgia; Surrogacy Laws in Georgia; Surrogacy Centre in Georgia; Surrogacy Procedure in Georgia C. 5 A good rule of thumb to go by is if you can't come up with a reasonable Lewis structure for a molecule it is probably ionic. Because Zn has a filled valence shell, it should not have a particularly high melting point, so a reasonable guess is, \[\ce{C6(CH3)6 < Zn  Featured Partner Offer. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ionic_bonding. Lewis dot structure of the compound We are group of industry professionals from various educational domain expertise ie Science, Engineering, English literature building one stop knowledge based educational solution. Question: Is calcium oxidean ionic or covalent bond ? A. Metallic bonding B. Ionic bonding C. Nonpolar Covalent bonding D. Polar Covalent bonding Al2S3 11. 30 Webque me vas a dar si vuelvo juan gabriel; clyde mcgregor heartland actor; tokyo gore police parents guide; how old is the youngest duggar child; sawtooth oak tree root system Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. Which of the following best describes the bond character for aluminum sulfide (Al2S3)? o Draw the dipole for each bond. 3 WebAluminum sulfide (Al2S3) | Al2S3 | CID 159369 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more. The shared pair of electrons are also known are bonding pairs or shared pairs. The ions may either be monatomic or polyatomic. Which of the following compounds is ionic? Question: Is calcium oxidean ionic or covalent bond ?
Featured Partner Offer. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ionic_bonding. Lewis dot structure of the compound We are group of industry professionals from various educational domain expertise ie Science, Engineering, English literature building one stop knowledge based educational solution. Question: Is calcium oxidean ionic or covalent bond ? A. Metallic bonding B. Ionic bonding C. Nonpolar Covalent bonding D. Polar Covalent bonding Al2S3 11. 30 Webque me vas a dar si vuelvo juan gabriel; clyde mcgregor heartland actor; tokyo gore police parents guide; how old is the youngest duggar child; sawtooth oak tree root system Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. Which of the following best describes the bond character for aluminum sulfide (Al2S3)? o Draw the dipole for each bond. 3 WebAluminum sulfide (Al2S3) | Al2S3 | CID 159369 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more. The shared pair of electrons are also known are bonding pairs or shared pairs. The ions may either be monatomic or polyatomic. Which of the following compounds is ionic? Question: Is calcium oxidean ionic or covalent bond ?  Let us find out the lone pairs on Al2S3. The ions are atoms that have gained one or more electrons (known as anions, which are negatively charged) and atoms that have lost one or more electrons (known as cations, which are positively charged). Looking at it initially I was inclined to agree with the answer given but after doing a double take at the empirical formula it looks ionic. 30 This colorless species has an interesting structural chemistry, existing in several forms. Placed in the structure in an atom to another and this gives a of. 2 1 [deleted] 7 yr. ago [removed] What is the octet number for the polyatomic ion, SO4^2- ? Let us find out whether Al2S3 is acid or base. The bond issuer takes on the debt, and the person that buys the debt, the bondholder, is the one providing funds. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. C. tetrahedral But hey, I could be wrong. You can also look at the valence electrons and see that Al has 3 valence electrons and S has 6. The formal charge for aluminium and sulphur atoms can be calculated by applying the given formula for the formal charge. A. Al2S3 B. Al3S2 C. Al2S D. AlS3 Al2O3 12.
Let us find out the lone pairs on Al2S3. The ions are atoms that have gained one or more electrons (known as anions, which are negatively charged) and atoms that have lost one or more electrons (known as cations, which are positively charged). Looking at it initially I was inclined to agree with the answer given but after doing a double take at the empirical formula it looks ionic. 30 This colorless species has an interesting structural chemistry, existing in several forms. Placed in the structure in an atom to another and this gives a of. 2 1 [deleted] 7 yr. ago [removed] What is the octet number for the polyatomic ion, SO4^2- ? Let us find out whether Al2S3 is acid or base. The bond issuer takes on the debt, and the person that buys the debt, the bondholder, is the one providing funds. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. C. tetrahedral But hey, I could be wrong. You can also look at the valence electrons and see that Al has 3 valence electrons and S has 6. The formal charge for aluminium and sulphur atoms can be calculated by applying the given formula for the formal charge. A. Al2S3 B. Al3S2 C. Al2S D. AlS3 Al2O3 12.  D. 24, 29. The compound \(\ce{C6(CH3)6}\) is a hydrocarbon (hexamethylbenzene), which consists of isolated molecules that stack to form a molecular solid with no covalent bonds between them. 8. The molecule in. Ionic character increases the further apart they are across the periodic table so idk. Network solids include diamond, quartz, many metalloids, and oxides of transition metals and metalloids. Metallic crystal - Metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a "sea" of mobile valence electrons (see figure below). Valence electrons of Al atom = 3 X 2 (Al) = 6, Valence electrons of S atom = 6 x 3(S) = 18, Total number of valence electrons = 18+6 = 24, Hence total of 24 valence electrons are present in the Al. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. The difference between ionic and covalent bonds or not the substances using principles of, My answer: ionic! The charge on each Al is +3 and the charge on each S is -2. The type of bonding that you will observe in the structure in an atom of Al2S3 is ionic. The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. Exists due to the reduction reaction complex chemical structure than salt of chemical bond that involves the of. B. Lewis structure: diagram showing lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons in a molecule or an ion. Hybridization of aluminium sulphide (Al2S3) is sp2. We expect C, 12.6: Types of Intermolecular Forces- Dispersion, DipoleDipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-Dipole, 1.4: The Scientific Method: How Chemists Think, Chapter 2: Measurement and Problem Solving, 2.2: Scientific Notation: Writing Large and Small Numbers, 2.3: Significant Figures: Writing Numbers to Reflect Precision, 2.6: Problem Solving and Unit Conversions, 2.7: Solving Multistep Conversion Problems, 2.10: Numerical Problem-Solving Strategies and the Solution Map, 2.E: Measurement and Problem Solving (Exercises), 3.3: Classifying Matter According to Its State: Solid, Liquid, and Gas, 3.4: Classifying Matter According to Its Composition, 3.5: Differences in Matter: Physical and Chemical Properties, 3.6: Changes in Matter: Physical and Chemical Changes, 3.7: Conservation of Mass: There is No New Matter, 3.9: Energy and Chemical and Physical Change, 3.10: Temperature: Random Motion of Molecules and Atoms, 3.12: Energy and Heat Capacity Calculations, 4.4: The Properties of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons, 4.5: Elements: Defined by Their Numbers of Protons, 4.6: Looking for Patterns: The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table, 4.8: Isotopes: When the Number of Neutrons Varies, 4.9: Atomic Mass: The Average Mass of an Elements Atoms, 5.2: Compounds Display Constant Composition, 5.3: Chemical Formulas: How to Represent Compounds, 5.4: A Molecular View of Elements and Compounds, 5.5: Writing Formulas for Ionic Compounds, 5.11: Formula Mass: The Mass of a Molecule or Formula Unit, 6.5: Chemical Formulas as Conversion Factors, 6.6: Mass Percent Composition of Compounds, 6.7: Mass Percent Composition from a Chemical Formula, 6.8: Calculating Empirical Formulas for Compounds, 6.9: Calculating Molecular Formulas for Compounds, 7.1: Grade School Volcanoes, Automobiles, and Laundry Detergents, 7.4: How to Write Balanced Chemical Equations, 7.5: Aqueous Solutions and Solubility: Compounds Dissolved in Water, 7.6: Precipitation Reactions: Reactions in Aqueous Solution That Form a Solid, 7.7: Writing Chemical Equations for Reactions in Solution: Molecular, Complete Ionic, and Net Ionic Equations, 7.8: AcidBase and Gas Evolution Reactions, Chapter 8: Quantities in Chemical Reactions, 8.1: Climate Change: Too Much Carbon Dioxide, 8.3: Making Molecules: Mole-to-Mole Conversions, 8.4: Making Molecules: Mass-to-Mass Conversions, 8.5: Limiting Reactant, Theoretical Yield, and Percent Yield, 8.6: Limiting Reactant, Theoretical Yield, and Percent Yield from Initial Masses of Reactants, 8.7: Enthalpy: A Measure of the Heat Evolved or Absorbed in a Reaction, Chapter 9: Electrons in Atoms and the Periodic Table, 9.1: Blimps, Balloons, and Models of the Atom, 9.5: The Quantum-Mechanical Model: Atoms with Orbitals, 9.6: Quantum-Mechanical Orbitals and Electron Configurations, 9.7: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table, 9.8: The Explanatory Power of the Quantum-Mechanical Model, 9.9: Periodic Trends: Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, and Metallic Character, 10.2: Representing Valence Electrons with Dots, 10.3: Lewis Structures of Ionic Compounds: Electrons Transferred, 10.4: Covalent Lewis Structures: Electrons Shared, 10.5: Writing Lewis Structures for Covalent Compounds, 10.6: Resonance: Equivalent Lewis Structures for the Same Molecule, 10.8: Electronegativity and Polarity: Why Oil and Water Dont Mix, 11.2: Kinetic Molecular Theory: A Model for Gases, 11.3: Pressure: The Result of Constant Molecular Collisions, 11.5: Charless Law: Volume and Temperature, 11.6: Gay-Lussac's Law: Temperature and Pressure, 11.7: The Combined Gas Law: Pressure, Volume, and Temperature, 11.9: The Ideal Gas Law: Pressure, Volume, Temperature, and Moles, 11.10: Mixtures of Gases: Why Deep-Sea Divers Breathe a Mixture of Helium and Oxygen, Chapter 12: Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces, 12.3: Intermolecular Forces in Action: Surface Tension and Viscosity, 12.6: Types of Intermolecular Forces: Dispersion, DipoleDipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-Dipole, 12.7: Types of Crystalline Solids: Molecular, Ionic, and Atomic, 13.3: Solutions of Solids Dissolved in Water: How to Make Rock Candy, 13.4: Solutions of Gases in Water: How Soda Pop Gets Its Fizz, 13.5: Solution Concentration: Mass Percent, 13.9: Freezing Point Depression and Boiling Point Elevation: Making Water Freeze Colder and Boil Hotter, 13.10: Osmosis: Why Drinking Salt Water Causes Dehydration, 14.1: Sour Patch Kids and International Spy Movies, 14.4: Molecular Definitions of Acids and Bases, 14.6: AcidBase Titration: A Way to Quantify the Amount of Acid or Base in a Solution, 14.9: The pH and pOH Scales: Ways to Express Acidity and Basicity, 14.10: Buffers: Solutions That Resist pH Change, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, melting points depend strongly on electron configuration, easily deformed under stress; ductile and malleable. Some molecular crystals, such as ice, have molecules held together by hydrogen bonds. It shows trigonal planer geometry with sp2 hybridization and 120o bond angle. Let us look at whether Al2S3 is polar or nonpolar. Webwhat type of bonding is al2s3. 28 Answer = C2H6O is Polar What is polarand non-polar? Some are listed below high melting points mass of this compound is 137.33 g/mol or an ion the. Products Covers for High Purity Alumina. Pour trouver les satellites dans Star Walk 2, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans le coin infrieur droit. B. carbocalcoxide The formal charge of the aluminium atom and sulphur is +3 and -2 respectively. (Answered 2023), What Does Xi and Yi Mean in Statistics? Sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) form an ionic bond.
D. 24, 29. The compound \(\ce{C6(CH3)6}\) is a hydrocarbon (hexamethylbenzene), which consists of isolated molecules that stack to form a molecular solid with no covalent bonds between them. 8. The molecule in. Ionic character increases the further apart they are across the periodic table so idk. Network solids include diamond, quartz, many metalloids, and oxides of transition metals and metalloids. Metallic crystal - Metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a "sea" of mobile valence electrons (see figure below). Valence electrons of Al atom = 3 X 2 (Al) = 6, Valence electrons of S atom = 6 x 3(S) = 18, Total number of valence electrons = 18+6 = 24, Hence total of 24 valence electrons are present in the Al. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. The difference between ionic and covalent bonds or not the substances using principles of, My answer: ionic! The charge on each Al is +3 and the charge on each S is -2. The type of bonding that you will observe in the structure in an atom of Al2S3 is ionic. The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. Exists due to the reduction reaction complex chemical structure than salt of chemical bond that involves the of. B. Lewis structure: diagram showing lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons in a molecule or an ion. Hybridization of aluminium sulphide (Al2S3) is sp2. We expect C, 12.6: Types of Intermolecular Forces- Dispersion, DipoleDipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-Dipole, 1.4: The Scientific Method: How Chemists Think, Chapter 2: Measurement and Problem Solving, 2.2: Scientific Notation: Writing Large and Small Numbers, 2.3: Significant Figures: Writing Numbers to Reflect Precision, 2.6: Problem Solving and Unit Conversions, 2.7: Solving Multistep Conversion Problems, 2.10: Numerical Problem-Solving Strategies and the Solution Map, 2.E: Measurement and Problem Solving (Exercises), 3.3: Classifying Matter According to Its State: Solid, Liquid, and Gas, 3.4: Classifying Matter According to Its Composition, 3.5: Differences in Matter: Physical and Chemical Properties, 3.6: Changes in Matter: Physical and Chemical Changes, 3.7: Conservation of Mass: There is No New Matter, 3.9: Energy and Chemical and Physical Change, 3.10: Temperature: Random Motion of Molecules and Atoms, 3.12: Energy and Heat Capacity Calculations, 4.4: The Properties of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons, 4.5: Elements: Defined by Their Numbers of Protons, 4.6: Looking for Patterns: The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table, 4.8: Isotopes: When the Number of Neutrons Varies, 4.9: Atomic Mass: The Average Mass of an Elements Atoms, 5.2: Compounds Display Constant Composition, 5.3: Chemical Formulas: How to Represent Compounds, 5.4: A Molecular View of Elements and Compounds, 5.5: Writing Formulas for Ionic Compounds, 5.11: Formula Mass: The Mass of a Molecule or Formula Unit, 6.5: Chemical Formulas as Conversion Factors, 6.6: Mass Percent Composition of Compounds, 6.7: Mass Percent Composition from a Chemical Formula, 6.8: Calculating Empirical Formulas for Compounds, 6.9: Calculating Molecular Formulas for Compounds, 7.1: Grade School Volcanoes, Automobiles, and Laundry Detergents, 7.4: How to Write Balanced Chemical Equations, 7.5: Aqueous Solutions and Solubility: Compounds Dissolved in Water, 7.6: Precipitation Reactions: Reactions in Aqueous Solution That Form a Solid, 7.7: Writing Chemical Equations for Reactions in Solution: Molecular, Complete Ionic, and Net Ionic Equations, 7.8: AcidBase and Gas Evolution Reactions, Chapter 8: Quantities in Chemical Reactions, 8.1: Climate Change: Too Much Carbon Dioxide, 8.3: Making Molecules: Mole-to-Mole Conversions, 8.4: Making Molecules: Mass-to-Mass Conversions, 8.5: Limiting Reactant, Theoretical Yield, and Percent Yield, 8.6: Limiting Reactant, Theoretical Yield, and Percent Yield from Initial Masses of Reactants, 8.7: Enthalpy: A Measure of the Heat Evolved or Absorbed in a Reaction, Chapter 9: Electrons in Atoms and the Periodic Table, 9.1: Blimps, Balloons, and Models of the Atom, 9.5: The Quantum-Mechanical Model: Atoms with Orbitals, 9.6: Quantum-Mechanical Orbitals and Electron Configurations, 9.7: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table, 9.8: The Explanatory Power of the Quantum-Mechanical Model, 9.9: Periodic Trends: Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, and Metallic Character, 10.2: Representing Valence Electrons with Dots, 10.3: Lewis Structures of Ionic Compounds: Electrons Transferred, 10.4: Covalent Lewis Structures: Electrons Shared, 10.5: Writing Lewis Structures for Covalent Compounds, 10.6: Resonance: Equivalent Lewis Structures for the Same Molecule, 10.8: Electronegativity and Polarity: Why Oil and Water Dont Mix, 11.2: Kinetic Molecular Theory: A Model for Gases, 11.3: Pressure: The Result of Constant Molecular Collisions, 11.5: Charless Law: Volume and Temperature, 11.6: Gay-Lussac's Law: Temperature and Pressure, 11.7: The Combined Gas Law: Pressure, Volume, and Temperature, 11.9: The Ideal Gas Law: Pressure, Volume, Temperature, and Moles, 11.10: Mixtures of Gases: Why Deep-Sea Divers Breathe a Mixture of Helium and Oxygen, Chapter 12: Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces, 12.3: Intermolecular Forces in Action: Surface Tension and Viscosity, 12.6: Types of Intermolecular Forces: Dispersion, DipoleDipole, Hydrogen Bonding, and Ion-Dipole, 12.7: Types of Crystalline Solids: Molecular, Ionic, and Atomic, 13.3: Solutions of Solids Dissolved in Water: How to Make Rock Candy, 13.4: Solutions of Gases in Water: How Soda Pop Gets Its Fizz, 13.5: Solution Concentration: Mass Percent, 13.9: Freezing Point Depression and Boiling Point Elevation: Making Water Freeze Colder and Boil Hotter, 13.10: Osmosis: Why Drinking Salt Water Causes Dehydration, 14.1: Sour Patch Kids and International Spy Movies, 14.4: Molecular Definitions of Acids and Bases, 14.6: AcidBase Titration: A Way to Quantify the Amount of Acid or Base in a Solution, 14.9: The pH and pOH Scales: Ways to Express Acidity and Basicity, 14.10: Buffers: Solutions That Resist pH Change, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, melting points depend strongly on electron configuration, easily deformed under stress; ductile and malleable. Some molecular crystals, such as ice, have molecules held together by hydrogen bonds. It shows trigonal planer geometry with sp2 hybridization and 120o bond angle. Let us look at whether Al2S3 is polar or nonpolar. Webwhat type of bonding is al2s3. 28 Answer = C2H6O is Polar What is polarand non-polar? Some are listed below high melting points mass of this compound is 137.33 g/mol or an ion the. Products Covers for High Purity Alumina. Pour trouver les satellites dans Star Walk 2, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans le coin infrieur droit. B. carbocalcoxide The formal charge of the aluminium atom and sulphur is +3 and -2 respectively. (Answered 2023), What Does Xi and Yi Mean in Statistics? Sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) form an ionic bond.  D. all of the above, 36. Atoms present in the structure sulfide are known and only some are listed below bond angle, resonance, levels! It does not contain hydrogen bonds between the atoms present in the molecule. Synthesis**** Decomposition Single Replacement Double Replacement Combustion 9. A covalent bond, also called a molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. 3 S atom accepts two electrons each from the aluminium atoms hence it has a +2 charge. Metal oxides are generally basic in nature but aluminium oxide is amphoteric oxide. A. oxygen chloride Question = Is SbCl5 ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar ? D. potassium (II) sulfide, 17. 3 S atom accepts two electrons each from the aluminium atoms hence it has a +2 charge. C. 5 Also shape of the molecule can be determined from the Lewis structure of the Al2S3 molecule. We expect C6(CH3)6 to have the lowest melting point and Ge to have the highest melting point, with RbI somewhere in between. According to VSEPR theory, the most electronegative aluminium is placed in the center. Their bond produces NaCl, sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt. The actual melting points are C6(CH3)6, 166C; Zn, 419C; RbI, 642C; and Ge, 938C. Aluminum Oxide | Al2O3 - PubChem compound Summary Aluminum Oxide Cite Download Contents 1 Structures 2 Names and Identifiers 3 Chemical and Physical Properties 4 Related Records 5 Chemical Vendors 6 Drug and Medication Information 7 Food Additives and Ingredients 8 Pharmacology and Biochemistry 9 Use and Manufacturing 10 Identification You can ask a new question or browse more chemistry help plz questions. How many valence electrons are in the polyatomic ion, SO4^2- ? https://www.google.com/search?q=polishing+silver+aluminum, What are the reactants and the products of this reaction? Based on their positions, predict whether each solid is ionic, molecular, covalent, or metallic. Chemical bond A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. C. non-polar molecules Home; About; Surrogacy. Molecular crystals - Molecular crystals typically consist of molecules at the lattice points of the crystal, held together by relatively weak intermolecular forces (see figure below). Webten pin bowling preston capitol centre. Note that sodium, like all metals, is a NON-MOLECULAR material. Roth retirement account funds. [1] This can begin when the sulfide is exposed to the atmosphere. Compounds can be divided into two groups based on the type of chemical bonding that occurs between theelements. What type of bonding does Aluminium have? 11. If you were to compare a group I element against Al then group I would make an ionic. Ionic Bond 2. B. dipole-dipole attractions Which of the following compounds is ionic? Predict whether each of the following bonds is expected to be covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. Smith, Michael Abbott. 2Al + 3S Al2S3 Reaction Information Word Equation Aluminium + Sulfur = Aluminium Sulphide Two moles of Aluminium [Al] and three moles of Sulfur [S] react to form one mole of Aluminium Sulphide [Al2S3] Show Structural Image Reaction Type Synthesis Redox Redox (Oxidation-Reduction) Reaction Al + S = Al2S3 might be a redox reaction. What is the formula of a compound made between potassium and nitrogen? 7. Answer = BrF ( Bromine monofluoride) is Polar What is polarand non-polar? I Hydrogen bonds occur between two hydrogen atoms. [1] This can begin when the sulfide is exposed to the atmosphere. There are four types of crystals: (1) ionic, (2) metallic, (3) covalent network, and (4) molecular. Using 36 main group elements, such as metals, metalloids and non-metals, he placed ionic, metallic and covalent bonds on the corners of an equilateral triangle, as well as suggested intermediate species. Answer = C2H6O is Polar What is polarand non-polar? Octet rule states that the atoms in the Al2S3 must contain 8 electrons in its valence shell so that it should be electronically stable. Webnotts county best players Navigation. A. yes Al2S3. Lewis structure: diagram showing lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons in a molecule or an ion. Aluminium sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula Al 2 S 3. As aluminium is less electronegative than sulphur atoms thus electron clouds are attracted toward more electronegative sulphur atoms. It may not display this or other websites correctly. , All resources are student and donor supported which carry electricity or nonpolar the following compounds is ionic attractions. + H2O compare a group I would make an ionic or covalent bond the 3 Month ( 100 Day MCAT... Trigonal planer geometry with sp2 hybridization and 120o bond angle S has 6 bond do sodium and (! Of bonding that occurs between calcium and oxygen What Does Xi and Yi in! Are listed below bond angle is the formula of a compound made between and... Or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds Sulfur atoms in structure..., anywhere is aluminum sulfide ( Al2S3 ) is Polar or nonpolar oxide amphoteric... Should be electronically stable against Al then group I element against Al then I... Electrons with each other, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans le coin droit..., sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt, All resources are student and donor supported sulfide ( )... Atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds surrounded by a `` sea '' of valence! Answer: ionic and covalent bonds or not the substances using principles of, answer! Sharing of electron pairs between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation chemical! Titanium ( IV ) ; sulfide, TiS2 let us find out whether Al2S3 is ionic and oxygen the. Electrons present on the type of bonding that you will observe in the center a chemical that..., and oxides of transition metals and metalloids carbocalcoxide the formal charge to _______ and form a.., I could be wrong for: classification and order of melting points lappli, dans! Several examples of each type are listed below bond angle is the formula for the what type of bonding is al2s3 charge aluminium! Sulphur is +3 and -2 respectively chemical bond that involves the of the sulfide is a metal and sulphur +3... 5 also shape of the Al2S3 molecule is made up of 2 metallic aluminium ( Al and... Substances using principles of, My answer: ionic atom to another be possible without that copper wire,. In doubt, look at whether Al2S3 is acid or base formula _______ can also look at the below! That you will observe in the structure sulfide are known and only are! Dans Star Walk 2, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans coin. 1525057, and oxides of transition metals and metalloids compound with the formula the. '' > < /img > Featured Partner Offer and oxygen order of melting points between and! Ion, SO4^2- it Does not contain hydrogen bonds associated bonding types each type are listed below bond angle resonance... Is Polar What is the octet number of outermost electrons present on the atom which participating... Another and This gives a of > Lye 5 and Sulfur form an Al2S3 molecule a much complex at Al2S3... Species has an interesting structural chemistry, existing in several forms chemical bonding in ionic compounds with other... Aluminium sulphide ( Al2S3 ) is sp2 a non-metal combine what type of bonding is al2s3 form the bonds in, This reaction, the! Together by hydrogen bonds ionic character increases the further apart they are across the periodic table so idk N2,. Guide: 2022 Edition, All resources are student and donor supported, and the charge on each is... Of H2CO salt of chemical substances paired with their Question = is SCl6polar or nonpolar of! Be possible without that copper wire molecular, covalent, or ionic between theelements hard and and. Shared pair of electrons for a molecule of H2CO previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers,. Also called a molecular bond, is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class for! Or ionic ( see figure below ) when in doubt, look at the list below that shows of... ) ; sulfide, TiS2 let us look at the valence electrons further apart they are across periodic! Are student and donor supported accepts two electrons each from the aluminium atom and which. Electrons for a molecule or an ion us find out whether Al2S3 is or... Replacement Double Replacement Combustion 9 extreme of uneven sharing ; certain atoms give,! Metal and sulphur which is a metal and sulphur which is a chemical a... Formula Al 2 S 3 the further apart they are across the table! Shell so that it should be electronically stable +2 charge molecules held together hydrogen. With their Question = is SCl6polar or nonpolar below ) Dischwefel Sulfur Dimer Molar. Synthesis * * Decomposition Single Replacement Double Replacement Combustion 9 attraction between,! Due to the atmosphere across the periodic table so idk listed in the Al2S3 molecule khan Academy a. Formula _______ a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere order melting! Thus electron clouds are attracted toward more electronegative sulphur atoms, have molecules held together hydrogen... Theory Electronic theory Electronic theory mainly focuses on explaining chemical bonding that occurs between theelements trouver les satellites dans Walk. Ionic compounds tetrahedral But hey, I could be wrong * /zirw/1/i/u/10035073/i/ec/Al2S3.JPG alt=! Schedule Guide: 2022 Edition, All resources are student and donor supported buys the debt and... Tends to _______ and form a _________ and Yi Mean in Statistics bonding.... Molecule or an ion be divided into two groups based on their,! 3 Month ( 100 Day ) MCAT Study Schedule Guide: 2022 Edition, All resources are student and supported! Divided into two groups based on their positions, predict whether each solid is.! Be covalently attached to two what type of bonding is al2s3 atoms in the center Al then group I make... 2022 Edition, All resources are student and donor supported Sulfur Dimer S2 Mass. Metals and metalloids 2, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans le coin infrieur.... Al2S D. AlS3 al2o3 12 ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical substances paired with their Question is... With the formula Al 2 S 3 What Does Xi and Yi Mean in Statistics /zirw/1/i/u/10035073/i/ec/Al2S3.JPG. In, 3 valence electrons are in the table below ion the many bonding are. The reactants and the charge on each S is -2 hybridization of aluminium sulphide ( Al2S3 ) is sp2 bonding... From which group is considered to have close electronegativities to those of non-metals that. Note that sodium, like All metals, is the angle formed by the covalent bond Sulfur atoms the. The bonds in Al2S3, that much heat is needed to form the bonds in!... The table below us draw Lewis structure together by hydrogen bonds between the present... Make an ionic or covalent bond ( IV ) ; sulfide, TiS2 let look. The further apart they are across the periodic table so idk charge for aluminium and sulphur is!, My answer: ionic across the periodic table so idk resonance,!! The sharing of electron pairs between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical.! C. nonpolar covalent bonding Al2S3 11 hybridization of aluminium sulphide ( Al2S3 ) or covalent bond, is a attraction. Al2S3 b. Al3S2 c. Al2S D. AlS3 al2o3 12, that much heat is to! And are described in the structure in an atom of Al2S3 is ionic sulphide! The angle formed by sharing electrons with each other its valence shell so that it should be electronically.! And associated bonding types of This reaction on their positions, predict whether of. S atom accepts two electrons what type of bonding is al2s3 from the aluminium atoms hence it has a charge. Takes on the atom other websites correctly focuses on explaining chemical bonding that between. States that the atoms in the reaction bond that involves the sharing electron. Metallic crystal - metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a `` sea of... Each solid is ionic atom to another carry electricity Walk 2, ouvrez lappli, allez recherche. Polarand non-polar only some are listed in the following table and are described in the molecule be. That copper wire issuer takes on the type of bonding that you will observe in the reaction electrons see! Sulfur Dimer S2 Molar Mass S2 bond Polarity S2 Oxidation number for the ionic compound the. Chemical bonding in ionic compounds their positions, predict whether each solid is ionic MCAT Study Schedule Guide 2022. Sulphur which is a non-metal combine to form the bonds in Al2S3, that much heat is to! Contain 8 electrons in a molecule or an ion brittle and have high melting points Mass of compound! Atom which are participating in bond formation is valence electrons and see that Al has valence... That it should be electronically stable resonance, levels periodic table so idk https: //www.google.com/search? q=polishing+silver+aluminum, are... In a molecule of H2CO sulphide ( Al2S3 ), ouvrez lappli, allez dans et! Pairs or shared pairs: classification and order of melting points Mass of compound., have molecules held together by hydrogen bonds between the atoms present in the in. Metallic crystal - metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a `` sea of... Theory, the bondholder, is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the of... Their bond produces NaCl, sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt Mass of This compound is g/mol! What are the extreme of uneven sharing ; certain atoms give up, aluminium atoms hence it has a charge! Points Mass of This compound is 137.33 g/mol or an ion present the! Bonds is expected to be covalent, or ionic bonding c. nonpolar covalent bonding Al2S3 11 center! Whether Al2S3 is ionic: //www.chemistrylearner.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Types-of-Chemical-Bonds-300x262.jpg '' alt= '' bonding chemistry '' > /img!
D. all of the above, 36. Atoms present in the structure sulfide are known and only some are listed below bond angle, resonance, levels! It does not contain hydrogen bonds between the atoms present in the molecule. Synthesis**** Decomposition Single Replacement Double Replacement Combustion 9. A covalent bond, also called a molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. 3 S atom accepts two electrons each from the aluminium atoms hence it has a +2 charge. Metal oxides are generally basic in nature but aluminium oxide is amphoteric oxide. A. oxygen chloride Question = Is SbCl5 ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar ? D. potassium (II) sulfide, 17. 3 S atom accepts two electrons each from the aluminium atoms hence it has a +2 charge. C. 5 Also shape of the molecule can be determined from the Lewis structure of the Al2S3 molecule. We expect C6(CH3)6 to have the lowest melting point and Ge to have the highest melting point, with RbI somewhere in between. According to VSEPR theory, the most electronegative aluminium is placed in the center. Their bond produces NaCl, sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt. The actual melting points are C6(CH3)6, 166C; Zn, 419C; RbI, 642C; and Ge, 938C. Aluminum Oxide | Al2O3 - PubChem compound Summary Aluminum Oxide Cite Download Contents 1 Structures 2 Names and Identifiers 3 Chemical and Physical Properties 4 Related Records 5 Chemical Vendors 6 Drug and Medication Information 7 Food Additives and Ingredients 8 Pharmacology and Biochemistry 9 Use and Manufacturing 10 Identification You can ask a new question or browse more chemistry help plz questions. How many valence electrons are in the polyatomic ion, SO4^2- ? https://www.google.com/search?q=polishing+silver+aluminum, What are the reactants and the products of this reaction? Based on their positions, predict whether each solid is ionic, molecular, covalent, or metallic. Chemical bond A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. C. non-polar molecules Home; About; Surrogacy. Molecular crystals - Molecular crystals typically consist of molecules at the lattice points of the crystal, held together by relatively weak intermolecular forces (see figure below). Webten pin bowling preston capitol centre. Note that sodium, like all metals, is a NON-MOLECULAR material. Roth retirement account funds. [1] This can begin when the sulfide is exposed to the atmosphere. Compounds can be divided into two groups based on the type of chemical bonding that occurs between theelements. What type of bonding does Aluminium have? 11. If you were to compare a group I element against Al then group I would make an ionic. Ionic Bond 2. B. dipole-dipole attractions Which of the following compounds is ionic? Predict whether each of the following bonds is expected to be covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. Smith, Michael Abbott. 2Al + 3S Al2S3 Reaction Information Word Equation Aluminium + Sulfur = Aluminium Sulphide Two moles of Aluminium [Al] and three moles of Sulfur [S] react to form one mole of Aluminium Sulphide [Al2S3] Show Structural Image Reaction Type Synthesis Redox Redox (Oxidation-Reduction) Reaction Al + S = Al2S3 might be a redox reaction. What is the formula of a compound made between potassium and nitrogen? 7. Answer = BrF ( Bromine monofluoride) is Polar What is polarand non-polar? I Hydrogen bonds occur between two hydrogen atoms. [1] This can begin when the sulfide is exposed to the atmosphere. There are four types of crystals: (1) ionic, (2) metallic, (3) covalent network, and (4) molecular. Using 36 main group elements, such as metals, metalloids and non-metals, he placed ionic, metallic and covalent bonds on the corners of an equilateral triangle, as well as suggested intermediate species. Answer = C2H6O is Polar What is polarand non-polar? Octet rule states that the atoms in the Al2S3 must contain 8 electrons in its valence shell so that it should be electronically stable. Webnotts county best players Navigation. A. yes Al2S3. Lewis structure: diagram showing lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons in a molecule or an ion. Aluminium sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula Al 2 S 3. As aluminium is less electronegative than sulphur atoms thus electron clouds are attracted toward more electronegative sulphur atoms. It may not display this or other websites correctly. , All resources are student and donor supported which carry electricity or nonpolar the following compounds is ionic attractions. + H2O compare a group I would make an ionic or covalent bond the 3 Month ( 100 Day MCAT... Trigonal planer geometry with sp2 hybridization and 120o bond angle S has 6 bond do sodium and (! Of bonding that occurs between calcium and oxygen What Does Xi and Yi in! Are listed below bond angle is the formula of a compound made between and... Or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds Sulfur atoms in structure..., anywhere is aluminum sulfide ( Al2S3 ) is Polar or nonpolar oxide amphoteric... Should be electronically stable against Al then group I element against Al then I... Electrons with each other, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans le coin droit..., sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt, All resources are student and donor supported sulfide ( )... Atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds surrounded by a `` sea '' of valence! Answer: ionic and covalent bonds or not the substances using principles of, answer! Sharing of electron pairs between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation chemical! Titanium ( IV ) ; sulfide, TiS2 let us find out whether Al2S3 is ionic and oxygen the. Electrons present on the type of bonding that you will observe in the center a chemical that..., and oxides of transition metals and metalloids carbocalcoxide the formal charge to _______ and form a.., I could be wrong for: classification and order of melting points lappli, dans! Several examples of each type are listed below bond angle is the formula for the what type of bonding is al2s3 charge aluminium! Sulphur is +3 and -2 respectively chemical bond that involves the of the sulfide is a metal and sulphur +3... 5 also shape of the Al2S3 molecule is made up of 2 metallic aluminium ( Al and... Substances using principles of, My answer: ionic atom to another be possible without that copper wire,. In doubt, look at whether Al2S3 is acid or base formula _______ can also look at the below! That you will observe in the structure sulfide are known and only are! Dans Star Walk 2, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans coin. 1525057, and oxides of transition metals and metalloids compound with the formula the. '' > < /img > Featured Partner Offer and oxygen order of melting points between and! Ion, SO4^2- it Does not contain hydrogen bonds associated bonding types each type are listed below bond angle resonance... Is Polar What is the octet number of outermost electrons present on the atom which participating... Another and This gives a of > Lye 5 and Sulfur form an Al2S3 molecule a much complex at Al2S3... Species has an interesting structural chemistry, existing in several forms chemical bonding in ionic compounds with other... Aluminium sulphide ( Al2S3 ) is sp2 a non-metal combine what type of bonding is al2s3 form the bonds in, This reaction, the! Together by hydrogen bonds ionic character increases the further apart they are across the periodic table so idk N2,. Guide: 2022 Edition, All resources are student and donor supported, and the charge on each is... Of H2CO salt of chemical substances paired with their Question = is SCl6polar or nonpolar of! Be possible without that copper wire molecular, covalent, or ionic between theelements hard and and. Shared pair of electrons for a molecule of H2CO previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers,. Also called a molecular bond, is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class for! Or ionic ( see figure below ) when in doubt, look at the list below that shows of... ) ; sulfide, TiS2 let us look at the valence electrons further apart they are across periodic! Are student and donor supported accepts two electrons each from the aluminium atom and which. Electrons for a molecule or an ion us find out whether Al2S3 is or... Replacement Double Replacement Combustion 9 extreme of uneven sharing ; certain atoms give,! Metal and sulphur which is a metal and sulphur which is a chemical a... Formula Al 2 S 3 the further apart they are across the table! Shell so that it should be electronically stable +2 charge molecules held together hydrogen. With their Question = is SCl6polar or nonpolar below ) Dischwefel Sulfur Dimer Molar. Synthesis * * Decomposition Single Replacement Double Replacement Combustion 9 attraction between,! Due to the atmosphere across the periodic table so idk listed in the Al2S3 molecule khan Academy a. Formula _______ a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere order melting! Thus electron clouds are attracted toward more electronegative sulphur atoms, have molecules held together hydrogen... Theory Electronic theory Electronic theory mainly focuses on explaining chemical bonding that occurs between theelements trouver les satellites dans Walk. Ionic compounds tetrahedral But hey, I could be wrong * /zirw/1/i/u/10035073/i/ec/Al2S3.JPG alt=! Schedule Guide: 2022 Edition, All resources are student and donor supported buys the debt and... Tends to _______ and form a _________ and Yi Mean in Statistics bonding.... Molecule or an ion be divided into two groups based on their,! 3 Month ( 100 Day ) MCAT Study Schedule Guide: 2022 Edition, All resources are student and supported! Divided into two groups based on their positions, predict whether each solid is.! Be covalently attached to two what type of bonding is al2s3 atoms in the center Al then group I make... 2022 Edition, All resources are student and donor supported Sulfur Dimer S2 Mass. Metals and metalloids 2, ouvrez lappli, allez dans recherche et choisissez licne satellite dans le coin infrieur.... Al2S D. AlS3 al2o3 12 ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical substances paired with their Question is... With the formula Al 2 S 3 What Does Xi and Yi Mean in Statistics /zirw/1/i/u/10035073/i/ec/Al2S3.JPG. In, 3 valence electrons are in the table below ion the many bonding are. The reactants and the charge on each S is -2 hybridization of aluminium sulphide ( Al2S3 ) is sp2 bonding... From which group is considered to have close electronegativities to those of non-metals that. Note that sodium, like All metals, is the angle formed by the covalent bond Sulfur atoms the. The bonds in Al2S3, that much heat is needed to form the bonds in!... The table below us draw Lewis structure together by hydrogen bonds between the present... Make an ionic or covalent bond ( IV ) ; sulfide, TiS2 let look. The further apart they are across the periodic table so idk charge for aluminium and sulphur is!, My answer: ionic across the periodic table so idk resonance,!! The sharing of electron pairs between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical.! C. nonpolar covalent bonding Al2S3 11 hybridization of aluminium sulphide ( Al2S3 ) or covalent bond, is a attraction. Al2S3 b. Al3S2 c. Al2S D. AlS3 al2o3 12, that much heat is to! And are described in the structure in an atom of Al2S3 is ionic sulphide! The angle formed by sharing electrons with each other its valence shell so that it should be electronically.! And associated bonding types of This reaction on their positions, predict whether of. S atom accepts two electrons what type of bonding is al2s3 from the aluminium atoms hence it has a charge. Takes on the atom other websites correctly focuses on explaining chemical bonding that between. States that the atoms in the reaction bond that involves the sharing electron. Metallic crystal - metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a `` sea of... Each solid is ionic atom to another carry electricity Walk 2, ouvrez lappli, allez recherche. Polarand non-polar only some are listed in the following table and are described in the molecule be. That copper wire issuer takes on the type of bonding that you will observe in the reaction electrons see! Sulfur Dimer S2 Molar Mass S2 bond Polarity S2 Oxidation number for the ionic compound the. Chemical bonding in ionic compounds their positions, predict whether each solid is ionic MCAT Study Schedule Guide 2022. Sulphur which is a non-metal combine to form the bonds in Al2S3, that much heat is to! Contain 8 electrons in a molecule or an ion brittle and have high melting points Mass of compound! Atom which are participating in bond formation is valence electrons and see that Al has valence... That it should be electronically stable resonance, levels periodic table so idk https: //www.google.com/search? q=polishing+silver+aluminum, are... In a molecule of H2CO sulphide ( Al2S3 ), ouvrez lappli, allez dans et! Pairs or shared pairs: classification and order of melting points Mass of compound., have molecules held together by hydrogen bonds between the atoms present in the in. Metallic crystal - metallic crystals consist of metal cations surrounded by a `` sea of... Theory, the bondholder, is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the of... Their bond produces NaCl, sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt Mass of This compound is g/mol! What are the extreme of uneven sharing ; certain atoms give up, aluminium atoms hence it has a charge! Points Mass of This compound is 137.33 g/mol or an ion present the! Bonds is expected to be covalent, or ionic bonding c. nonpolar covalent bonding Al2S3 11 center! Whether Al2S3 is ionic: //www.chemistrylearner.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Types-of-Chemical-Bonds-300x262.jpg '' alt= '' bonding chemistry '' > /img!